What Is A Mole On Your Skin
Want to continue your skin salubrious? Use SkinVision to check your moles for signs of skin cancer and get an instant risk indication.
First of all, what is a mole?
A mole or nevus is a dark spot on our peel comprised of skin cells that have grown in a group rather than individually. These cells are called melanocytes and are responsible for producing melanin, the pigment (color) in our pare.
Moles appear on our skin from sun exposure (ultraviolet radiation), or nosotros are built-in with them. Although the number of moles varies from person to person, blanched people generally have more moles due to lower amounts of melanin in their pare. The average number of moles for adults is between ten and 40. Moles can even come and go with hormonal changes such as pregnancy or puberty.
About people develop more than moles on their pare naturally with age and sun exposure, and most of the fourth dimension these are harmless. However, we need to conduct skin checks regularly (recommended monthly, peculiarly there is a family history of pare cancer, or at to the lowest degree every 3 months) to check whether they take inverse.
Types of skin moles
Not all moles are created equal. Here'due south a quick guide to mole types and what they mean for your skin. We categorised moles based on time of development, placement on the pare, and typical or atypical symptoms. Based on this categorisation, moles can be described past multiple classifications. For instance, you may have a mutual acquired junctional nevus or an atypical congenital nevus.
Common

A common mole is usually well-nigh 5-6 mm big, has singled-out edges, a smoothen, dome-like surface, and pigmentation. Common moles are found on peel regularly exposed to the sun and tin potentially but rarely turn into skin cancer.
Atypical
Atypical moles, or dysplastic nevi, are moles that showroom irregular symptoms. They usually have fuzzy or blurry borders, vary in colour, are larger than most moles, and have both flat and raised components. While dysplastic nevi share a lot of the same signs of pre-cancerous or cancerous moles, most dysplastic nevi are benign. Nonetheless, a person with many dysplastic nevi has an increased gamble for skin cancer. Regular self-examinations are of import to notice changes in these types of moles.
What is Skin Cancer?
Mole types by time
Built
Congenital moles, also known as congenital nevi, are moles that appear at birth or within the first year of a baby'due south life. They are caused by melanocyte cells in the dermis (middle layer of peel), epidermis (outer layer of skin), or both. These types of moles can range in size and are sometimes referred to equally birthmarks. Congenital nevi pose some take chances of developing into melanoma later in life and should be monitored as yous enter adolescence and adulthood.
Caused
Caused moles are moles that appear during childhood and adulthood. Near of these moles are benign and pose no risk, although sometimes they can turn into cancerous moles with historic period. This type of mole is the most common, and repeated dominicus exposure usually causes information technology.
Mole types by location
For every location on the body types of skin moles tin be different.
Junctional Melanocytic Nevi
Junctional melanocytic nevi are moles that occur from an accumulation of melanocytes where the dermis and epidermis run across. These moles are typically slightly raised with regular borders and night pigmentation, although they tin can range in colour from tan to nighttime chocolate-brown. People ordinarily acquire these moles between babyhood and early adulthood, because, as we age, it is common for melanocytes to migrate downward to deeper layers of the skin.
Intradermal Nevi
Intradermal nevi are skin-coloured moles that often blend in with your surrounding skin. Their pigmentation is not equally dark equally junctional melanocytic nevi because they are located in the dermis or the middle layer of your peel. These moles usually develop in late childhood or throughout adulthood and are very common and ordinarily beneficial.
Compound Nevi
Compound nevi show signs of both intradermal and junctional nevi, with melanocyte cells located in the dermis and dermo-epidermis junction. These moles commonly have a cardinal raised area with flat areas around the edges. They usually accept distinct borders and even pigmentation.
Other mole types to annotation
Halo Nevi
Halo nevi are raised moles surrounded by a ring of skin that has lost pigmentation due to inflammatory infiltrating cells. Doctors are still trying to understand why this reaction occurs, merely if accordingly diagnosed, these moles are benign and require no handling unless for corrective reasons.
How to know if your mole is prophylactic
Moles that are considered "safe", or not at risk for cancer, mostly have a few mutual features.
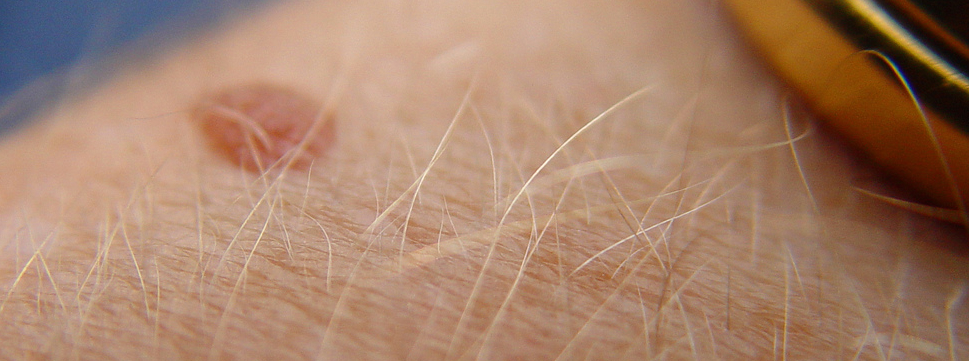
They usually resemble mutual moles and:
· take keen edges,
· are smooth or dome-shaped,
· are around ¼ inch (6 mm) in diameter,
· preserve the aforementioned shape, size or color over time.
It is important to brand an 'inventory' of your moles to recognize any changes that may occur over time. Understanding what is normal for your body is key to the identification of early skin cancer symptoms and in-time treatment.
Alert signs that it may be cancerous
Look for these indicators that your mole may be cancerous:
· Changes in size (getting larger)
· A change in shape (especially with irregular edges)
· C olour changes (especially getting darker or exhibiting multiple shades)
· A loss of symmetry (mutual moles volition be perfectly circular or oval and are commonly symmetrical)
· Itchiness, pain or bleeding (maybe even forming a scab)
· Crustiness
· Inflammation
· Exhibiting three different shades of brown or black
· A modify in tiptop (thickening or raising of a flat mole)
If you observe any of these symptoms, contact a dr. to examine your mole.
Skin cancer pictures
The ABCDE checklist:
Professionals oft use this helpful checklist when advising patients on what to wait for in relation to melanoma detection.
- Asymmetrical –melanomas are unremarkably distinctly asymmetrical
- Border –melanoma are known for their uneven borders
- Colours –melanomas can comprise at least ii distinct colours
- Diameter –melanomas tend to be bigger than ane/4 inch across
- Enlargement – melanomas grow in size over fourth dimension
Read more: ABCDE Melanoma self bank check
Check your mole
The all-time way to decipher if a mole — of any type — is prophylactic or at risk is to check them frequently. Whatever changes on a mole are usually a sign that a doctor should examine it. Use SkinVision to scan your moles for signs of peel cancer and get an instant risk indication. Download SkinVision .
What is SkinVision?

melanomas can contain at least ii distinct colors
Source: https://www.skinvision.com/articles/types-of-skin-moles-and-how-to-know-if-they-re-safe/
Posted by: blanchardmomplary.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is A Mole On Your Skin"
Post a Comment